Crimped Fin Tube
Crimped fin tubes for enhanced heat transfer and mechanical strength.
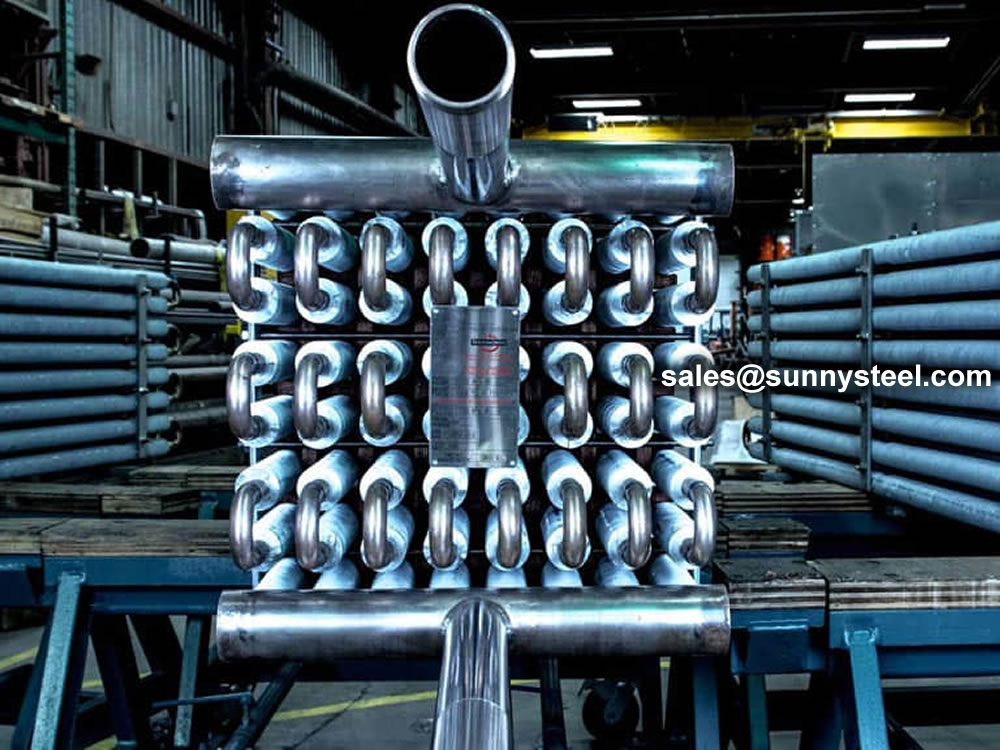
Fin tubes are used in applications involving the transfer of heat from a hot fluid to a colder fluid through a tube wall.
Furthermore, finned tubes are used when the heat transfer coefficient on the outside of the tubes is appreciably lower than that on the inside.
Finned Heat Exchanger Pipes are integral components in various thermal systems, designed to improve heat transfer between fluids by increasing the surface area of the pipes. These pipes have external fins attached to their surface, which helps in dissipating heat more efficiently. The fins can be made from materials like aluminum, copper, or steel, depending on the application's requirements. Finned pipes are used in industries like HVAC, power generation, petrochemical processing, and refrigeration, where efficient heat exchange is critical. Their design varies according to the specific needs of the system they are part of.
A finned tube heat exchanger is an important component in many heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, as well as industrial processes that require efficient heat transfer.
The key importance of a finned tube heat exchanger includes:

End user, EPC companies, Trading companies. Manufacturers of air cooler, fire heater, heat exchanger, marine boiler, economizer, power plant boiler, HRSG boiler, waste heat revovery unit, air heater etc. Our end user are mainly from these industrial sectors: power plant, refinery & petrochemical, Offshore & marine.
When the heat transfer coefficient of the fluid inside the tube is several times larger than that of fluid outside the tube (for example steam inside and oil outside), the overall heat transfer rate can be greatly improved by increasing the outside surface of the tube. In mathematical terms, the product of heat transfer coefficient for the outside fluid multiplied by the outside surface area is made to more closely match the product of the inside fluid heat transfer coefficient multiplied by the inside surface area.
So the whole concept of finned tubes is to increase the outside surface area of the tube. As an example, a finned tube configuration of 2” (nominal, 2.375” actual) pipe with a ¾” high welded helical solid fin of 12 gauge thickness with 6 fins per inch has an outside surface area of 8.23 sq. ft. per linear foot; whereas the same bare pipe has an outside surface area of only.62 sq. ft. per linear foot. That is a 13X increase in outside surface area. See Design Information for extensive tables of surface areas and fin weights.
The rate at which such heat transfer can occur depends on three factors:
“In many cases, one fin tube
replaces six or more bare tubes
at less than 1/3 the cost and 1/4 the volume.”
By increasing the outside surface area of the tube, the overall heat transfer rate is increased, thereby reducing the total number of tubes required for a given application. This reduces the overall equipment size and the cost of the project. In many cases, one finned tube replaces six or more bare tubes at less than 1/3 the cost and ¼ the volume.
In other words, the heat transferred from liquid to gas, vapor to gas, such as steam to air heat ex-changer, and thermic fluid to air heat ex changer. According to different materials and fabrication process, there are several kinds of fin tubes, such as extruded fin tube, crimped spiral fin tube, G type embedded fin tube, L/KL/LL Foot Fin Tube, etc.
Used as heat transfer element, fin tubes are usually working under high temperature with flue gas. For example, the condition for boiler heat ex-changer fin tube is very bad, high temperature, high pressure in corrosive atmosphere. In this case, the finned tubes should have a high performances.
They are widely used in food processing, timber drying, dyeing and printing industry, paper mill plant, pipeline transport, gas recovery, gas pre-heater, textile industry, power transfer, etc.
Generally, tubes equipped with surface enhancing devices, such as fins or grooves, are used where heat exchange is required between two fluids whose ability to transmit calories is very far apart. For a water / air exchange, for example, the local exchange coefficient on the water side is much higher than that on the air side. Thus, fins are added to the surface in contact with air in order to increase the density of the heat flux between the two fluids.
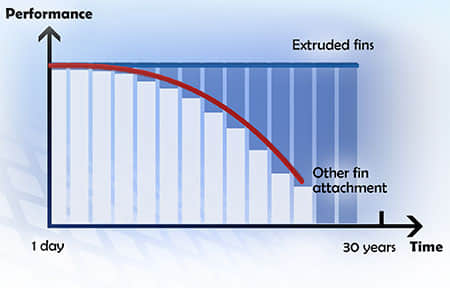
Being the only interface between the hot and cold source, the extruded finned tube is at the heart of heat transfer. Its quality plays a key role in the ability of an exchanger to efficiently transfer thermal energy between the two fluids. More precisely, the way in which the fin is secured to the tube affects the efficiency of the exchanger in the short, medium and long term.
Indeed, studies have shown that the main cause of the loss of efficiency of an exchanger is due to a loss of quality of the fin attachment to the tube. Indeed, after a few thermal cycle, a gap between the fins and the tubes occurs due to thermal expansion and vibrations.
According to the heat exchange application and operation, there are various materials.
The common ones are Aluminum, Alloy, Copper, Brass, Nickel, Titanium, Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, etc, among which the aluminum and alloy are mostly used.
The basic performance for fin tube heat exchange should be with good solder ability and form ability, higher mechanical strength, good corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity. In spite of these, aluminum and alloy are also featured in extension and higher tensile strength increases under lower temperature. Around all world, especially for low temperature and compact heat exchange, they are widely applied.
Let’s see the feature of aluminum
1. Low Density
By alloying and heat treatment, it can reach the structural of construction steel. Suitable for various transportation, especially for small vehicle, reducing weight and consumption.
2. Good Corrosion Resistance
When under harsh conditions, the materials oxide from aluminum is non-toxic. With aluminum heat exchange, no worries that air or liquid inside will be destructed by oxide after long time.
3. Good Thermal Conductivity
Especially suitable for radiating fin, heat transfer evaporator and condenser.
4. High Yielding and resistance to die cutting.
It is easy for processing and forming.
As a professional finned tube manufacturer, our leading product is aluminum finned tube. Should you have any interest, please contact us for more.
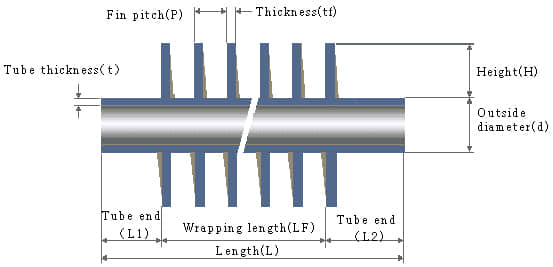
When the fins are root-grounded on the base bare tube, in the case of heat from inside to outside, the heat will be transferred from fin root along fin height. It is also continuously transmitted to the surrounding fluid by convective heat transfer. As a result, the fin temperature gradually decreases along the altitude. This also illustrates that difference between fin temperature and ambient fluid temperature is reducing gradually and the heat change per unit is shrinking. Therefore, the effect of fin surface area on enhanced heat transfer is decreasing. The higher the fin, the contribution of the increased area to heat exchange is smaller.
Generally speaking, as for the high frequency welded fin tube applied in engineering project, when fin height is 15mm, the fin efficiency is about 0.8; when fin height is 20mm, the fin efficiency is decreased to 0.7. Based on this, 15mm is the best height. If fins height above 20mm, the fin efficiency will be very bad, so generally not adopted. However, for the aluminum fin on air cooler, height at 22-25mm are always adopted due to much better heat conductivity coefficient of aluminum than carbon steel.
How will fin pitch affect fin ratio?
Usually smaller pitch can effectively increase fin ratio. While considering the flow gas property and ash deposit, we should pay attention to following factors.
A. Serious heavy ash deposit
Such as electric furnace and converter in steel works and exhaust of industrial cellar furnace, the ash content is heavy. If fin tubes are used for heat exchange, larger fin pitch will be suggested. For example, if pitch above 10mm, it is necessary to add a air discharge and choose an air blower.
B. Occasion with small ash deposit but should also be cared.
Take exhaust on plant boiler and industrial boiler as example, 8mm fin pitch is suitable, but should be designed with self-blowing ability.
C. Occasion with no dust or light dust.
Such as exhaust on burning natural gas equipment or air cooler, fin pitch at 4-6mm is OK. For aluminum air cooler, 3mm as fin pitch is also chosen.
The choice on fin thickness depends on corrosion and abrasion of fluid gas. Usually thicker fin is used on site with heavy corrosion.
Aluminum extruded fin tube is widely applied in barley malt, paper mill, timber drying, tobacco, food processing, coal mining, petrochemical, chemical fiber, construction materials, printing and dyeing, as more than 30 industries.
Meantime, they are also complementing for equipment such as air conditioner, drying oven, drying room, air coolers and so on.
Extruded aluminum fin tube is rolled as an integrity with no thermal contact resistance, high intensity, featured in thermal shock and mechanical shock resistance. Heat exchangers assembled with this kind of fin tube (extruded fin type) is much better than the one equipped with string fin tubes or hectically wound fin tubes (L/LL/KL type fin).
Extruded Aluminum Finned Tubes, also known as “Integral Finned Tubes”. Integral finned tubes are manufactured by rolling process on tubes. During finning operation, the inside diameter of the tubes is reduced and helical fins are rolled on the tube wall. The tubes material can be Copper Alloy, Brass Alloys, Copper Nickel Alloy, Titanium Alloy, Stainless Steel, Duplex Stainless Steel etc. The pressure required to extrude fins from the aluminum sleeve creates an excellent “pressure bond” between the two materials.
Copper and aluminum com-posited fin tubes are rolled from a muff copper tube, advantaged in tight link, small thermal resistance, good heat transfer efficiency, small flow loss and strong corrosion resistance. When working in long time under heating and cooling conditions, they are durable and not easy to deform.
The integral extruded fin tubes is smooth on surface and easy to clean. When wet cooling in heating and air conditioning project, it is easy to remove the condensation water on the outer surface of the fin, and it is not easy to dust and scale in the heating and other heat exchange.
The fin strip is wound into a machined groove and securely locked into place by back filling with the base tube.
G fin tube consists of aluminum fin strip that is mechanically embedded into the wall of the tube. The embedding process is controlled by tooling that first plows a groove into the tubes outside diameter, then guides the base of the fin into the groove and finally locks the fin in place by rolling the groove closed on the base of the fin. This ensures that maximum heat transfer is maintained at high tube metal temperature 400°C.
The aluminum fin strip or the copper fin strip is folded into an L shape and spirally wound tightly under the action of tension on the outer surface of the base tube. Tension in the fin strip is wrapped around the tube serves to make the fin foot forcefully on the tube, thus hold the fin firmly in place.
An L-shaped foot, 1/16″ wide, is first formed on one side of the fin strip (hence the name L-Foot). The strip is then wound tightly around the tube, with the foot bearing on the tube outer surface. A typical fin spacing is 10 fins per inch of tube length — this can be varied. Tension in the fin strip as it is wrapped around the tube serves to seat the fin foot forcefully on the tube, and to hold the fin firmly in place.
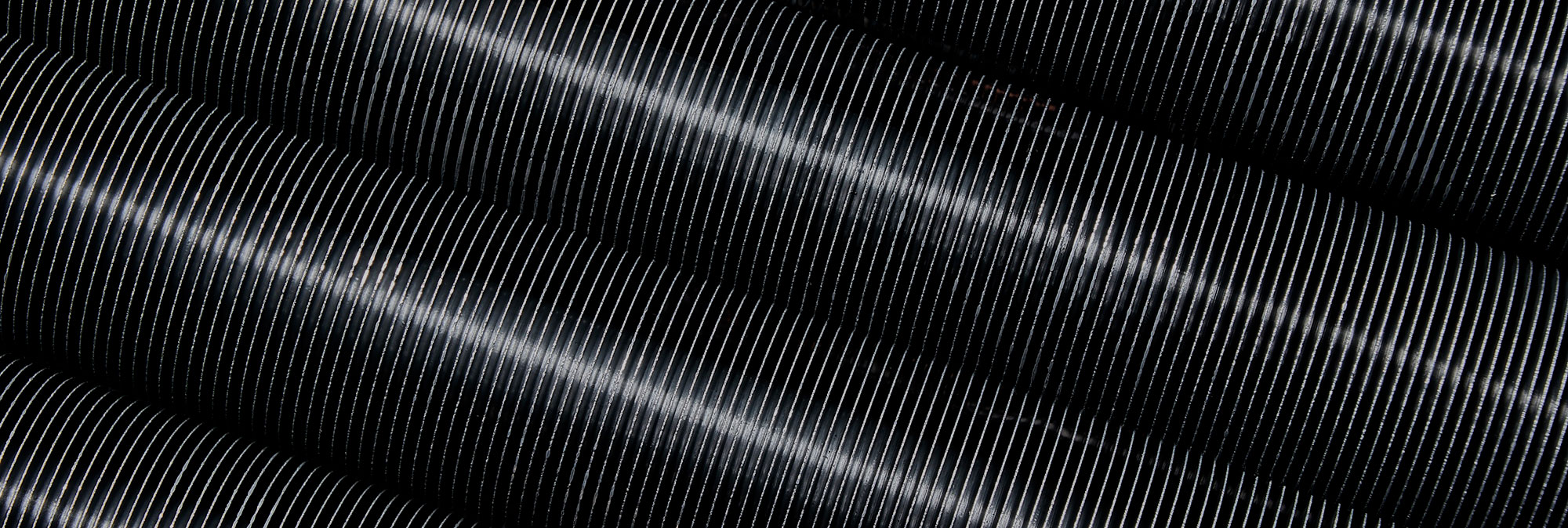
Extruded aluminum finned tubes, also known as “integral finned tubes”. Integral finned tubes are manufactured by rolling process on tubes. During finning operation, the inside diameter of the tubes is reduced and helical fins are rolled on the tube wall.

When you partner with Sunny Steel, you can stop worrying about meeting deadlines thanks to our responsive and timely service. You'll also say goodbye to unnecessary shopping around. Instead, you'll get white glove service from an expert who understands your needs and can get you the materials you need quickly.
