ASTM A335 P91
ASTM A335 P91 alloy pipe, known for its high creep strength and resistance to high-temperature exposure.
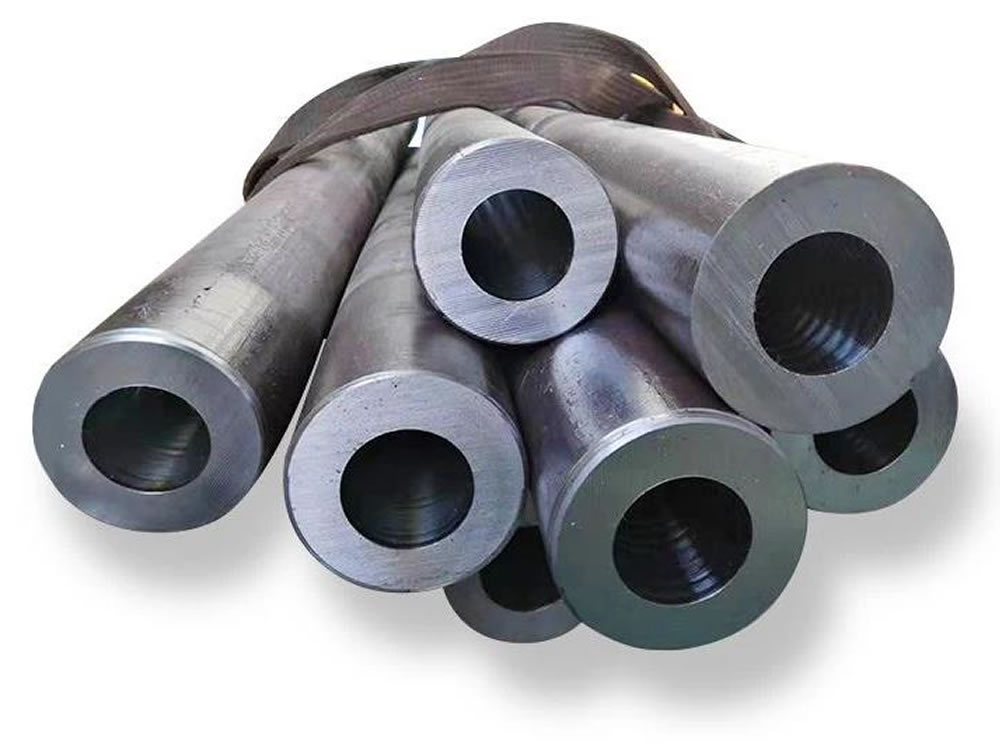

ASTM A335 Pipe (ASME S/A335, Chorme-Moly) is a seamless ferritic Alloy-Steel Pipe for high temperature service.
ASTM A335 is commonly used for power generation, refineries, and petrochemical industries, especially in high-temperature service applications. Below are the equivalents of ASTM A335 in other standards:
ASTM A335/ASME SA335 is a specification that covers seamless ferritic alloy steel pipe for high-temperature service. It includes various grades of chrome moly alloy pipes, such as P1, P5, P9, P11, P12, P22, P91, and others.
If you are comparing specific grades within ASTM A335, such as P11 or P22, they have equivalents in other standards:
While ASTM A335/ASME SA335 pipes are designed for high-temperature service, equivalent standards like DIN 17175 and EN 10216-2 can be used in different international markets, depending on project needs. Contact us for specific details on grades and equivalents that best suit your application.
Also known as 1.25Cr-0.5Mo, the UNS designation of ASTM A335 P11 is K11597. Its ASTM equivalent includes ASTM A369 FP11 as well as ASTM A213 T11.
ASTM A335 is used for the manufacturing of seamless ferritic alloy-steel pipe designed for high-temperature service. It finds applications in various industries, primarily where high-temperature and high-pressure conditions are encountered. Some common uses of ASTM A335 pipes include:
Power Plants: They are used for the construction of boilers, superheaters, and heat exchangers in thermal power plants.
Refineries: ASTM A335 pipes are employed for high-temperature processes in oil refineries, such as cracking units and distillation columns.
Petrochemical Industry: They are utilized in the production of petrochemicals and chemicals, particularly in high-temperature reactions.
Chemical Processing: These pipes find use in various chemical processes that involve elevated temperatures.
High-Temperature Service: Any application where pipes need to withstand high temperatures, making them suitable for power generation and industrial processes.
Overall, ASTM A335 pipes are essential in industries where the combination of high-temperature resistance and strength is crucial for safe and efficient operations.
Length: 6 meters, 12 meters or customized. ASTM A335 P11 Pipe (ASME SA335 P11) is Chrome Moly Alloy Seamless Pipe that used for high-temperature services, P11 Grade Pipe Chrome content at 1.00% to 1.50%, Moly content 0.44% to 0.65%, Minimum tensile strength 415MPa, minimum yield strength 205Mpa.
ASTM A333 and ASTM A335 are both standards set by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), but they cover different types of steel pipes intended for different applications. Here are the key differences between ASTM A333 and ASTM A335:
Purpose:
Alloying Elements:
Temperature Range:
Applications:
According to ASTM International, ASTM A335 is the standard specification for seamless Ferritic Alloy-Steel Pipe for High Temperature Service. This specification covers pipes with alloy material, manufactured in seamless form, and with nominal wall and minimum wall thickness.
Pipe ordered to this specification shall be suitable for bending, flanging (vanstoning), and similar forming operations, and for fusion welding. Sometimes referred to as “P Grade”, chome moly pipe is popular in P-Grades P5, P9, P11, P22, and P91.
ASTM A335 standard is issued under the fixed designation A 335/A 335M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.
The most common use of grades P11, P22, and P91 is in the power industry and petro-chemical plants, Grades P5 and P9 are commonly used in refineries.
ASTM A335 is often called as chrome moly pipe because of the chemical contain of Molybdenum (Mo) and Chromium (Cr). Molybdenum increases the strength of steel and Chromium (or chrome) is the essential constituent of stainless steel.
The composition chrome moly alloy steel pipe make it ideal for use in power plants, refineries, petro chemical plants, and oil field services where fluids and gases are transported at extremely high temperatures and pressures.
Yes, it is known for its ability to handle high-pressure environments effectively.
While it can be prone to corrosion, proper coatings can make it highly resistant.
It is produced through a seamless manufacturing process, ensuring its robustness.
The seamless construction eliminates potential weak points, making it more reliable under pressure.
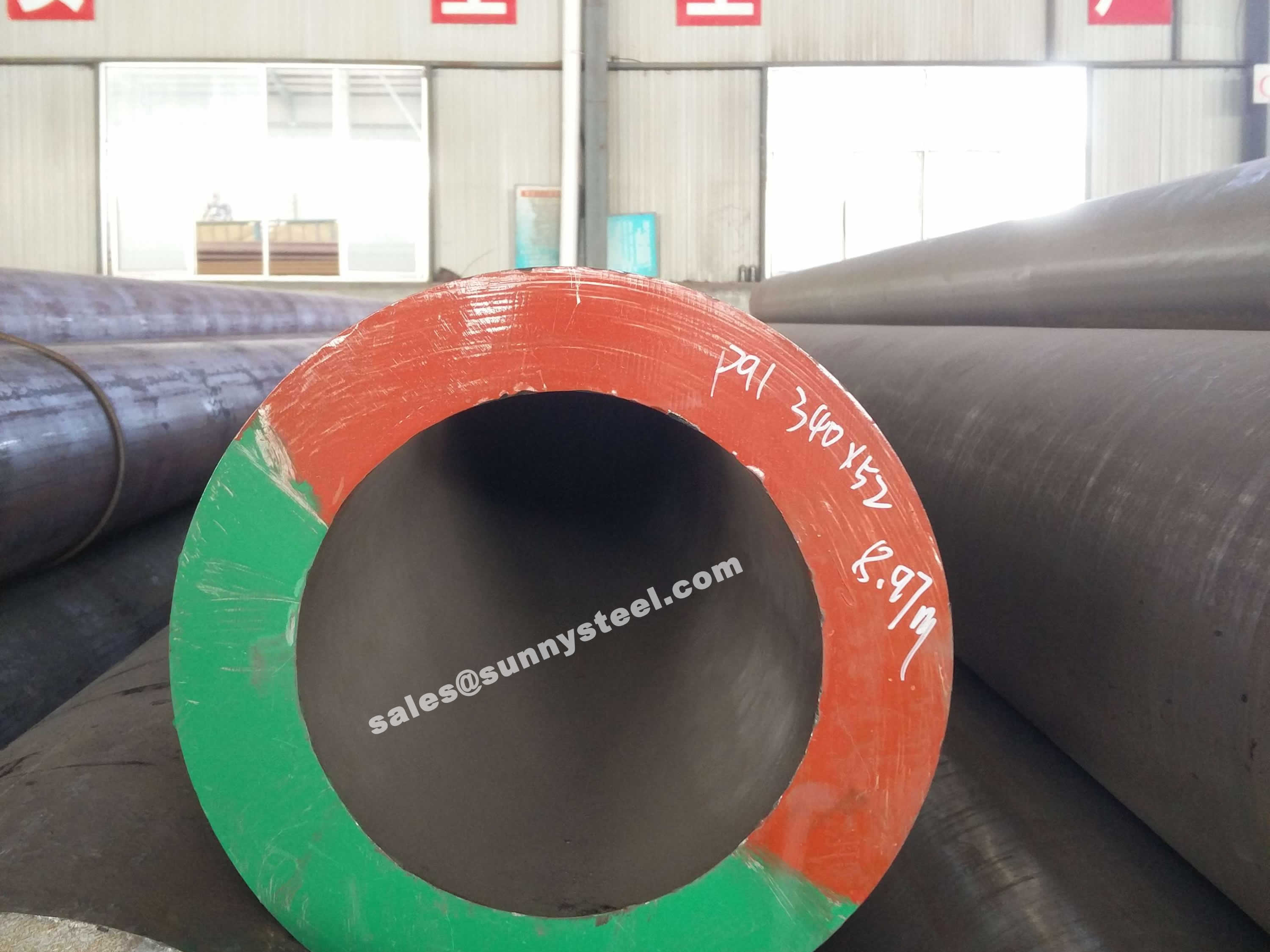

ASTM A335 is a standard specification for seamless ferritic alloy-steel pipe intended for high-temperature service.
This material is commonly used in power plants, refineries, and other industrial settings where high-temperature and high-pressure conditions are encountered. The "A" in ASTM A335 stands for "alloy," indicating that the pipe is made from alloy steel, which typically includes elements such as chromium, molybdenum, and sometimes vanadium to enhance its high-temperature properties.
1 This specification covers nominal wall and minimum wall seamless ferritic alloy-steel pipe intended for high-temperature service. Pipe ordered to this specification shall be suitable for bending, flanging (vanstoning), and similar forming operations, and for fusion welding. Selection will depend upon design, service conditions, mechanical properties, and high-temperature characteristics.
2 Several grades of ferritic steels (see Note 1) are covered. Their compositions are given in Table 1.
Note 1.. Ferritic steels in this specification are defined as low- and intermediate-alloy steels containing up to and including 10% chromium.
3 Supplementary requirements (S1 to S7) of an optional nature are provided. These supplementary requirements call for additional tests to be made, and when desired, shall be so stated in the order together with the number of such tests required.
4 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the specification. The inch-pound units shall apply unless the "M" designation of this specification is specified in the order.
Note The dimensionless designator NPS (nominal pipe size) has been substituted in this standard for such traditional terms as "nominal diameter", "size", and "nominal size".
ASTM A335 Seamless Steel Pipe is generally named chrome moly pipe for the chemical elements- Molybdenum and Chromium. Molybdenum improves steel performances as steel strength, elastic limit, wear resistance, impact and hardenability.
ASTM A335 seamless steel pipe is a popular choice for high-temperature applications due to several key reasons:
In summary, ASTM A335 seamless steel pipe is popular in high-temperature applications due to its high-temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, high strength, good weldability, uniform properties, and cost-effectiveness. Its combination of properties makes it an ideal choice for use in various high-temperature and high-pressure applications, especially in the power generation, chemical processing, and oil and gas industries.
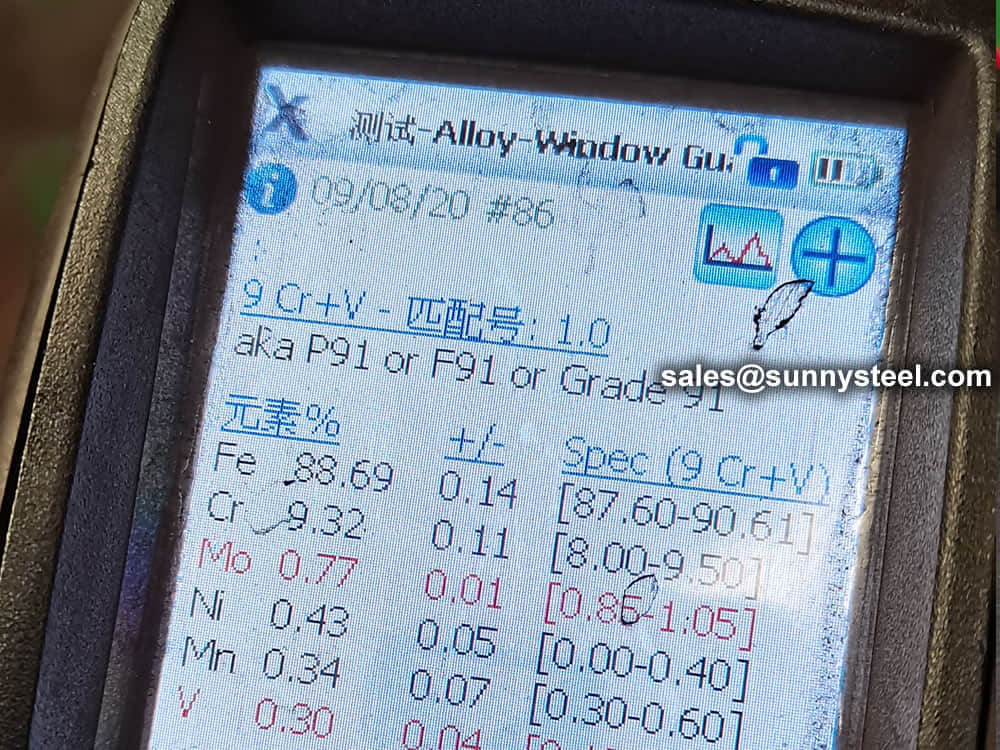
ASTM Specification pipe confirming to ASTM A335 shall have the following chemical properties. Tensile and Hardness Requirements The tensile properties of the ASTM A335 pipe shall conform to the requirements as prescribed. Pipe of Grades P91, P92, and P122 shall have a hardness not exceeding 250 HB/265 HV [25 HRC]. For pipe of Grades P91, P92, P122, and P911, Brinell, Vickers, or Rockwell hardness tests shall be made on a specimen from each lot (see Note 7). These pipe bear high resistance to rupture at high temperature and pressures. With hydrogen crack resistance and sulfide stress corrosion cracking chrome moly pipe are highly preferred over Carbon pipe.
| Grade | C | Mn | P max | S max | Si | Cr | Mo | V | N | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 0.1-0.2 | 0.3-0.8 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.1-0.5 | 1.0-1.5 | 0.44-0.65 | / | / | / |
| P2 | 0.1-0.2 | 0.3-0.61 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.1-0.3 | 0.5-0.81 | 0.44-0.65 | / | / | / |
| P5 | ≤0.15 | 0.3-0.6 | 0.025 | 0.025 | ≤0.5 | 4.0-6.0 | 0.45-0.65 | / | / | / |
| P5b | ≤0.15 | 0.3-0.6 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 1.0-2.0 | 4.0-6.0 | 0.45-0.65 | / | / | / |
| P5c | ≤0.12 | 0.3-0.6 | 0.025 | 0.025 | ≤0.5 | 4.0-6.0 | 0.45-0.65 | / | / | / |
| P9 | ≤0.15 | 0.3-0.6 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.25-1.0 | 8.0-10.0 | 0.9-1.1 | / | / | / |
| P11 | 0.05-0.15 | 0.3-0.6 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.5-1.0 | 1.0-1.5 | 0.44-0.65 | / | / | / |
| P12 | 0.05-0.15 | 0.3-0.61 | 0.025 | 0.025 | ≤0.5 | 0.8-1.25 | 0.44-0.65 | / | / | / |
| P15 | 0.05-0.15 | 0.3-0.6 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 1.15-1.65 | / | 0.44-0.65 | / | / | / |
| P21 | 0.05-0.15 | 0.3-0.6 | 0.025 | 0.025 | ≤0.5 | 2.65-3.35 | 0.8-1.06 | / | / | / |
| P22 | 0.05-0.15 | 0.3-0.6 | 0.025 | 0.025 | ≤0.5 | 1.9-2.6 | 0.87-1.13 | / | / | / |
| P23 | 0.04-0.1 | 0.1-0.6 | 0.03 | 0.01 | ≤0.5 | 1.9-2.6 | 0.05-0.3 | 0.2-0.3 | ≤0.015 | Cb(0.02-0.08) ,B(0.001-0.006) |
| Al(≤0.03), W(1.45-1.75) | ||||||||||
| Ni(≤0.4), Ti(0.005-0.060) | ||||||||||
| P24 | 0.05-0.1 | 0.3-0.7 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.15-0.45 | 2.2-2.6 | 0.9-1.1 | 0.2-0.3 | ≤0.012 | Ti(0.06-0.1), Al(≤0.02) |
| B(0.0015-0.007) | ||||||||||
| P36 | 0.1-0.17 | 0.8-1.2 | 0.03 | 0.025 | 0.25-0.50 | ≤0.30 | 0.25-0.50 | ≤0.02 | ≤0.02 | Ni(1.0-1.3), Cu(0.5-0.8) |
| Cb(0.015-0.045), Al(≤0.050) | ||||||||||
| P91 | 0.08-0.12 | 0.3-0.6 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.2-0.5 | 8.0-9.5 | 0.85-1.05 | 0.18-0.25 | 0.03-0.07 | Ni(≤0.4), Al(≤0.02), Cb(0.06-0.1) |
| Ti(≤0.01), Zr(≤0.01) | ||||||||||
| P92 | 0.07-0.13 | 0.3-0.6 | 0.02 | 0.01 | ≤0.50 | 8.5-9.5 | 0.3-0.6 | 0.15-0.25 | 0.03-0.07 | Ni(≤0.4), AL(≤0.02), Cb(0.04-0.09) |
| W(1.5-2.0), B(0.001-0.006) | ||||||||||
| Ti(≤0.01), Zr(≤0.01) | ||||||||||
| P122 | 0.07-0.14 | ≤0.7 | 0.02 | 0.01 | ≤0.50 | 10.0-11.5 | 0.25-0.6 | 0.15-0.3 | 0.04-0.1 | Ni(≤0.5), Al(≤0.02), Ti(≤0.01) |
| W(1.5-2.5), Cu(0.3-1.7), Zr(≤0.01) | ||||||||||
| Cb(0.04-0.1), B(0.0005-0.005) | ||||||||||
| P911 | 0.09-0.13 | 0.3-0.6 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.1-0.5 | 8.5-9.5 | 0.9-1.1 | 0.18-0.25 | 0.04-0.09 | Ni(≤0.4), Cb(0.06-0.1) |
| B(0.0003-0.006),Al(≤0.02) | ||||||||||
| W(0.9-1.1),Ti(≤0.01),Zr(≤0.01) |
ASTM A335 pipe may be either hot finished or cold drawn with the finishing treatment as required in Grade P2 and P12 – The steel shall be made by coarse- grain melting practice. Specific limits, if any, on grain size or deoxidation practice shall be a matter of agreement between the manufacturer and purchaser.
| Werkstoff /DIN | EN | ASTM |
|---|---|---|
| 1.5415 | 16Mo3 | A335 Grade P1 |
| 1.7335 | 13CrMo4-5 | A335 Grade P11, P12 |
| 1.738 | 10CrMo9-10 | A335 Grade P22 |
| 1.7362 | X11CrMo5 | A335 Grade P5 |
| A335 Grade P9 | ||
| 1.4903 | X10CrMoVNb9-1 | A335 Grade P91 |
| Tensile Strength, min., psi | P-5 | P-9 | P-11 | P-22 | P-91 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ksi | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 85 |
| MPa | 415 | 415 | 415 | 415 | 585 |
| Yield Strength, min., psi | |||||
| ksi | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 60 |
| MPa | 205 | 205 | 205 | 205 | 415 |
Product Analysis At the request of the purchaser, an analysis of two pipe from each lot shall be made by the manufacturer. A lot of ASTM A335 pipe shall consist of the following: NPS Designator Under 2 400 or fraction thereof 2 to 5 200 or fraction thereof 6 and over 100 or fraction thereof. Note: ASTM A335 P91 shall not have a hardness not exceeding 250 HB/265 HV [25HRC].
| Grade | Tensile strength | Yield strength |
|---|---|---|
| P1,P2 | 380 | 205 |
| P12 | 415 | 220 |
| P23 | 510 | 400 |
| P91 | 585 | 415 |
| P92,P11 | 620 | 440 |
| P122 | 620 | 400 |
It also enhances the corrosion resistance of steel, and inhibits pitting. Chromium (or chrome) is the essential constituent of stainless steel. Any steel with 12% or more Chrome is considered stainless. Chrome is virtually irreplaceable in resisting oxidation at elevated temperatures. Chrome raises the tensile, yield, and hardness at room temperatures. The composition chrome moly alloy steel pipe make it ideal for use in power plants, refineries, petro chemical plants, and oil field services where fluids and gases are transported at extremely high temperatures and pressures.
| Grade | Heat Treatment Type P5, P9, P11, and P22 |
Normalizing Temperature Range F [C] | Subcritical Annealing or Tempering Temperature Range F [C] |
|---|---|---|---|
| A335 P5 (b,c) | Full or Isothermal Anneal | ||
| Normalize and Temper | ***** | 1250 [675] | |
| Subcritical Anneal (P5c only) | ***** | 1325 – 1375 [715 - 745] | |
| A335 P9 | Full or Isothermal Anneal | ||
| Normalize and Temper | ***** | 1250 [675] | |
| A335 P11 | Full or Isothermal Anneal | ||
| Normalize and Temper | ***** | 1200 [650] | |
| A335 P22 | Full or Isothermal Anneal | ||
| Normalize and Temper | ***** | 1250 [675] | |
| A335 P91 | Normalize and Temper | 1900-1975 [1040 - 1080] | 1350-1470 [730 - 800] |
| Quench and Temper | 1900-1975 [1040 - 1080] | 1350-1470 [730 - 800] |
With years of expertise, we provide a diverse array of steel tube processing options. From sawing and machining tube blanks to intricate bending and upsetting operations, we actively assist you throughout your projects.
Our capabilities extend to eccentricity reduction and concentricity enhancement through turning and grinding. We excel in creating complex geometries using processes like rotary swaging and axial forming. Additionally, we offer property modifications via partial heat treatment, ensuring tailored solutions for your specific needs.












Chemical composition inspection, mechanical properties test(tensile strength,yield strength, elongation, flaring, flattening, bending, hardness, impact test), surface and dimension test,no-destructive test, hydrostatic test.
identification of the chemical composition of the metal used to manufacture the fitting. Uses PMI sensors, including X-ray fluorescence or optical emission spectrometry.
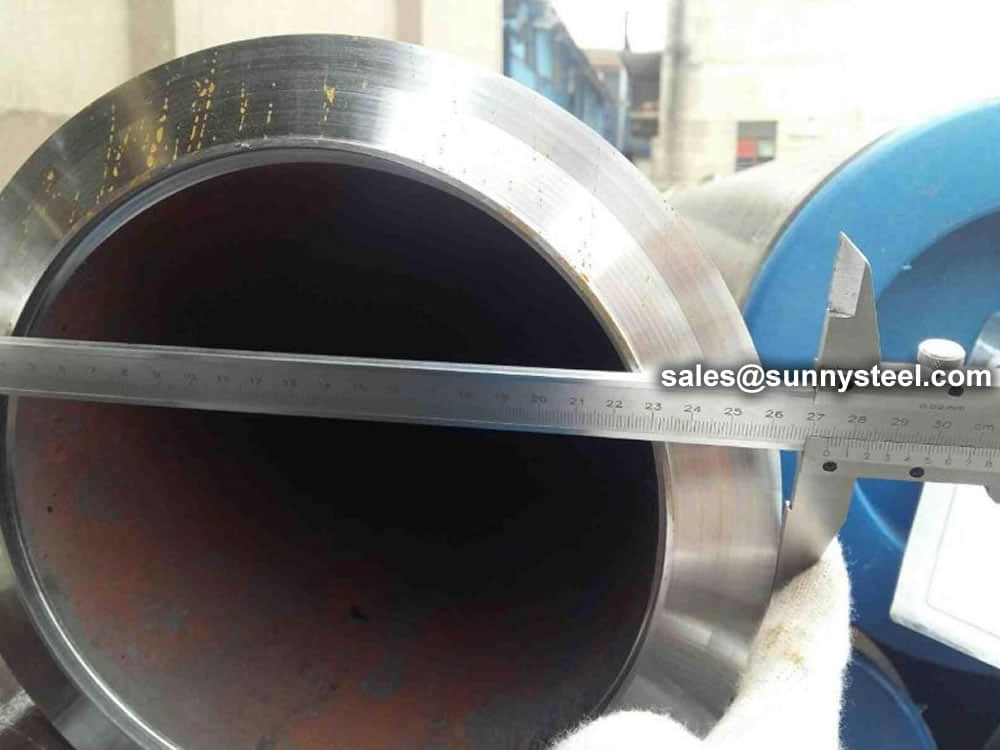
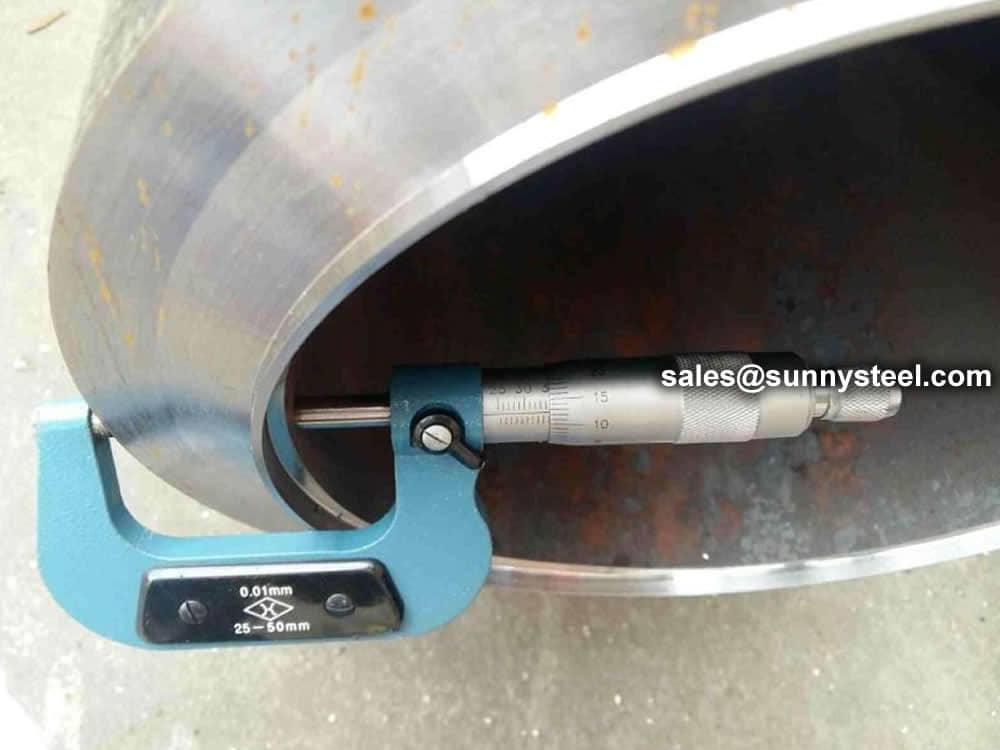
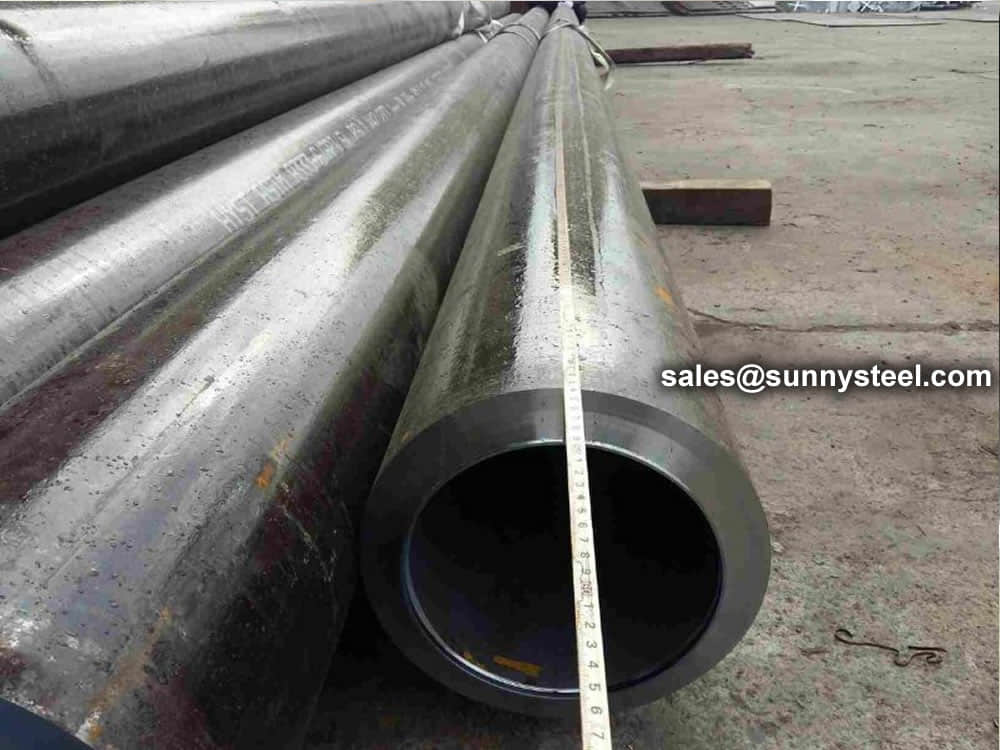
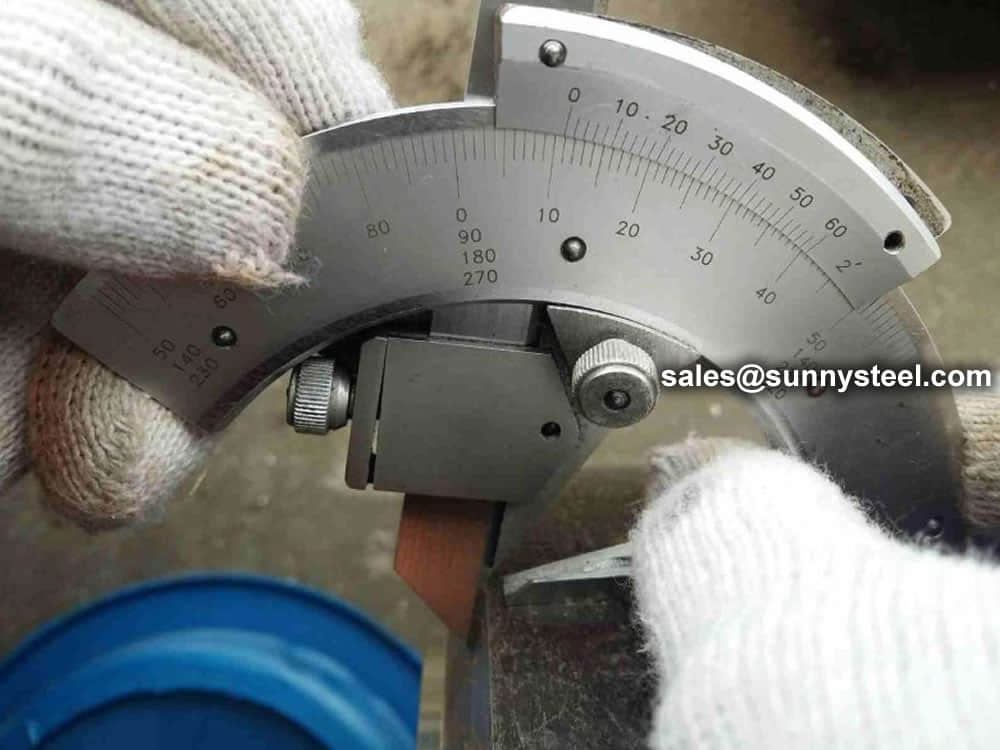
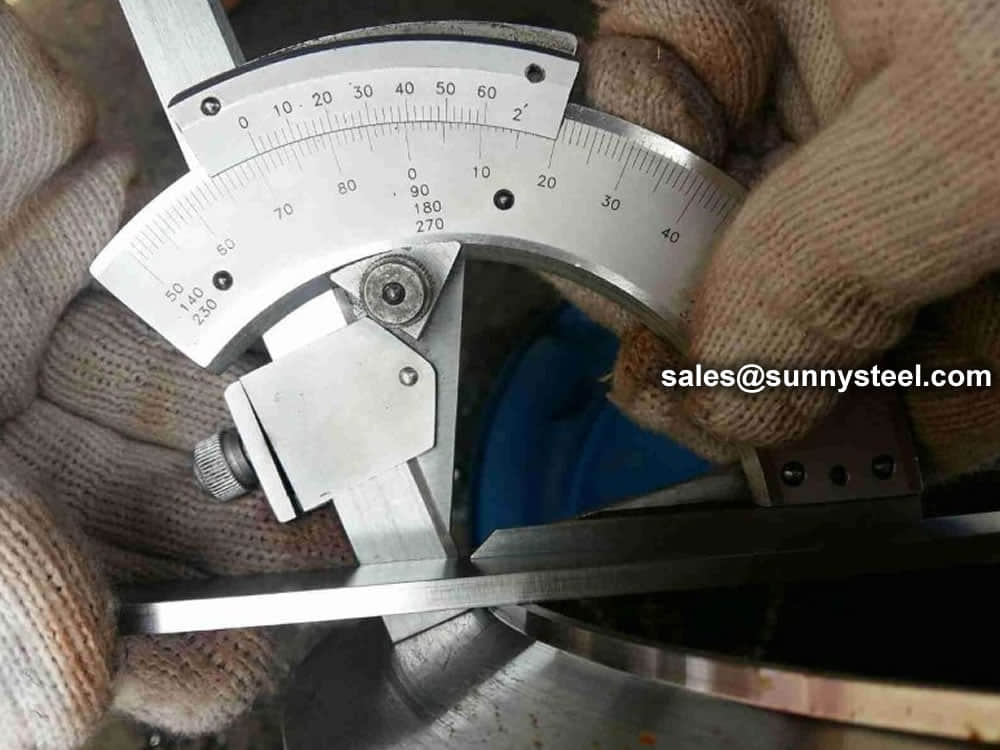
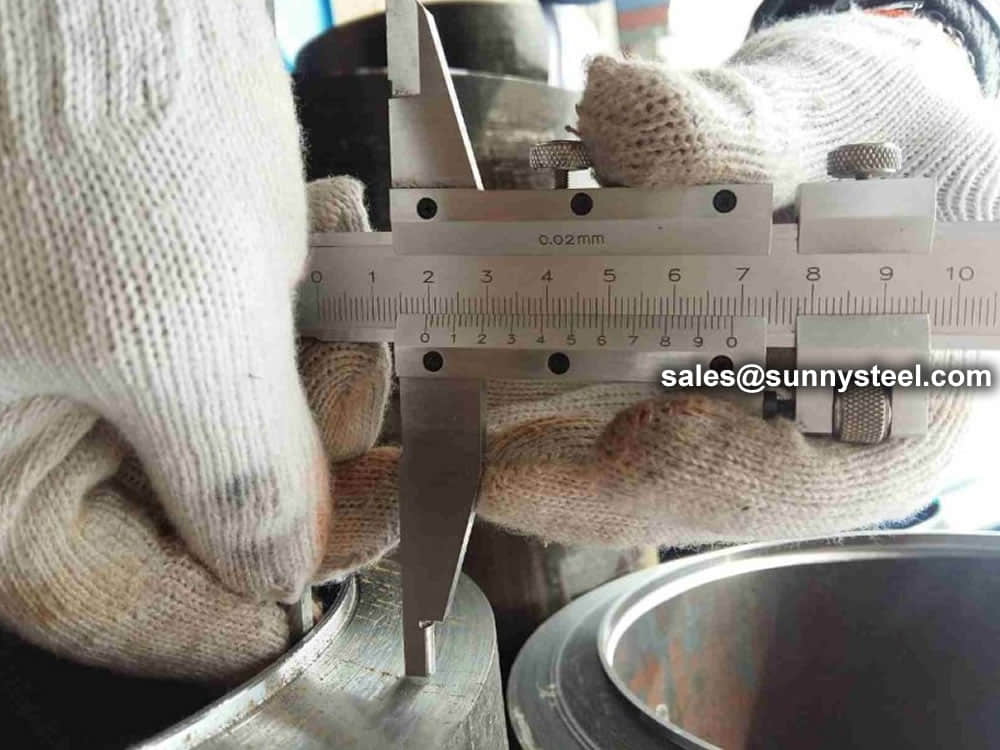
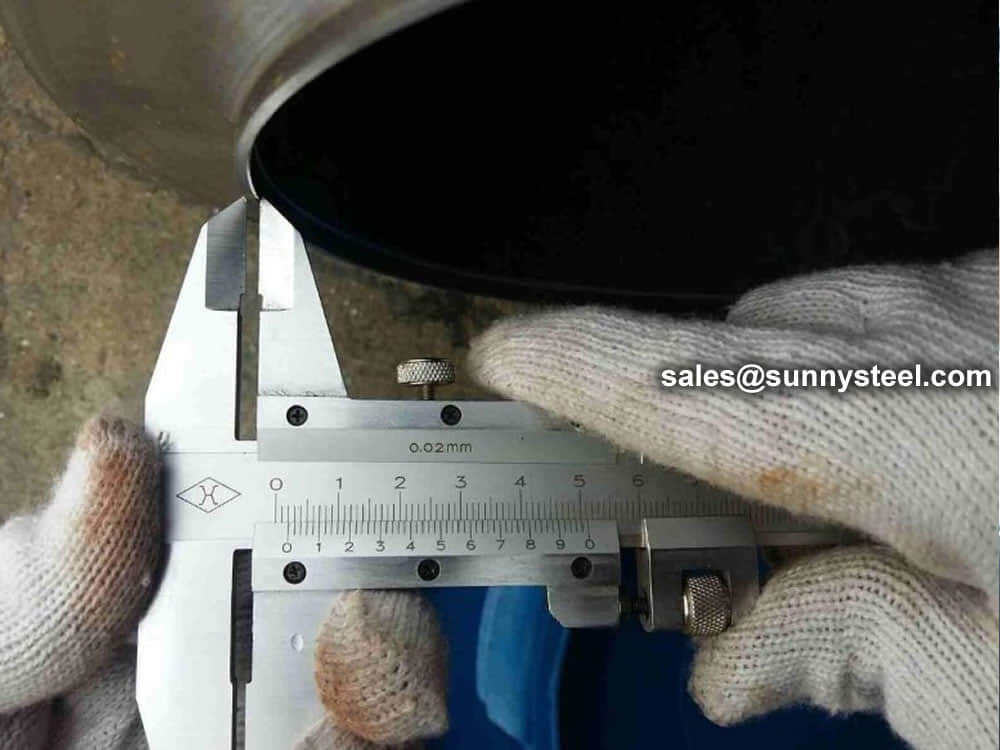
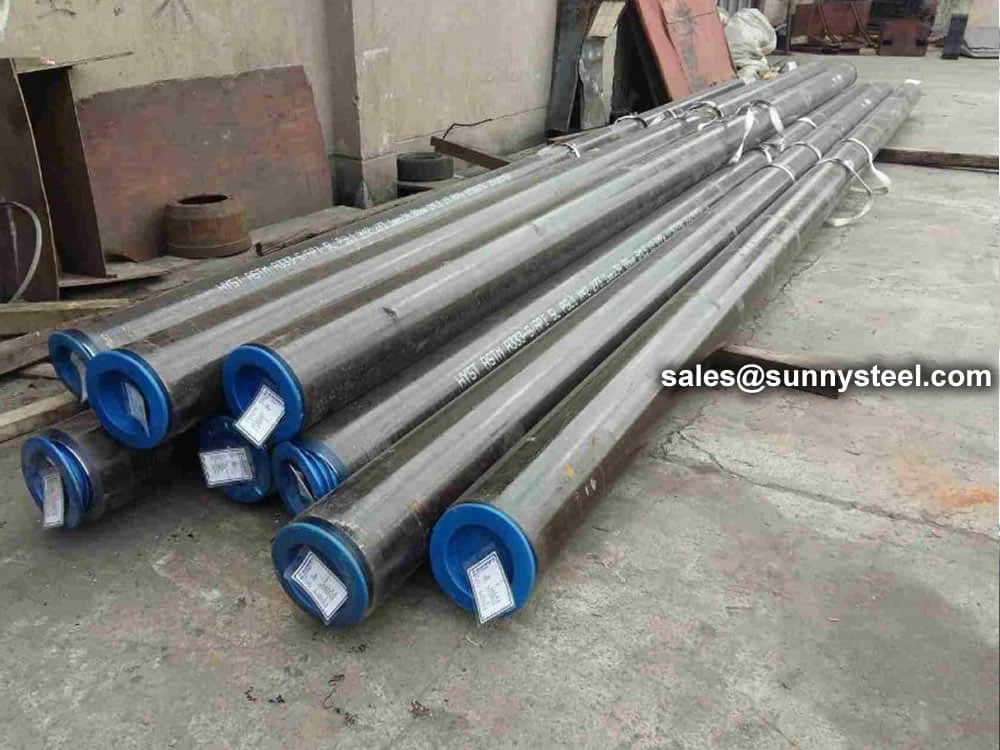
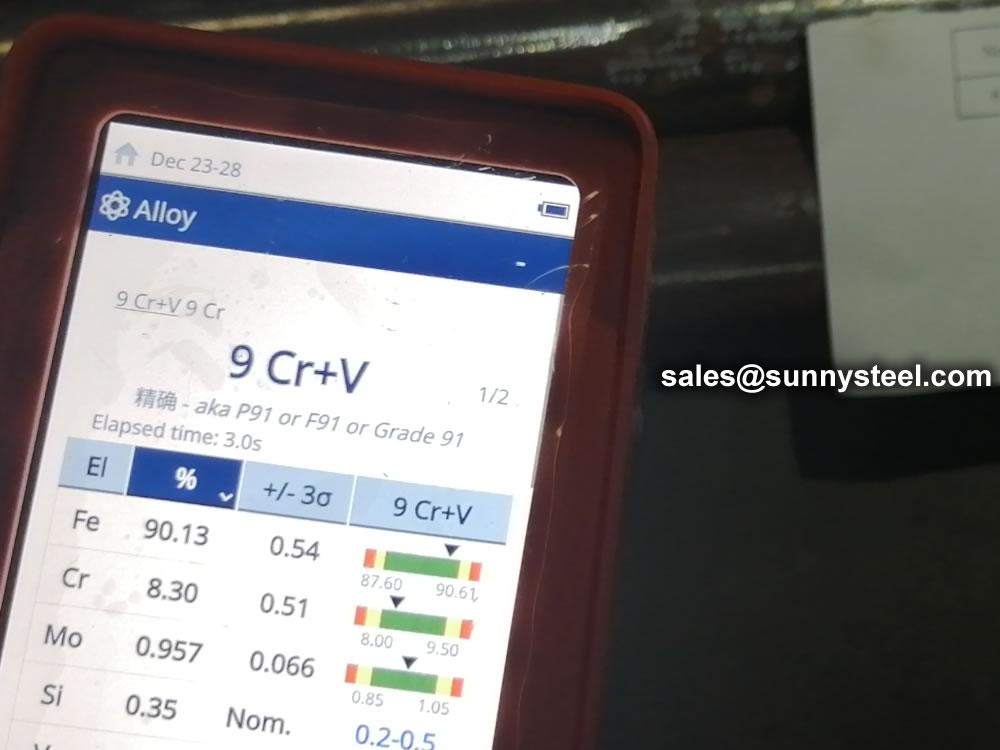
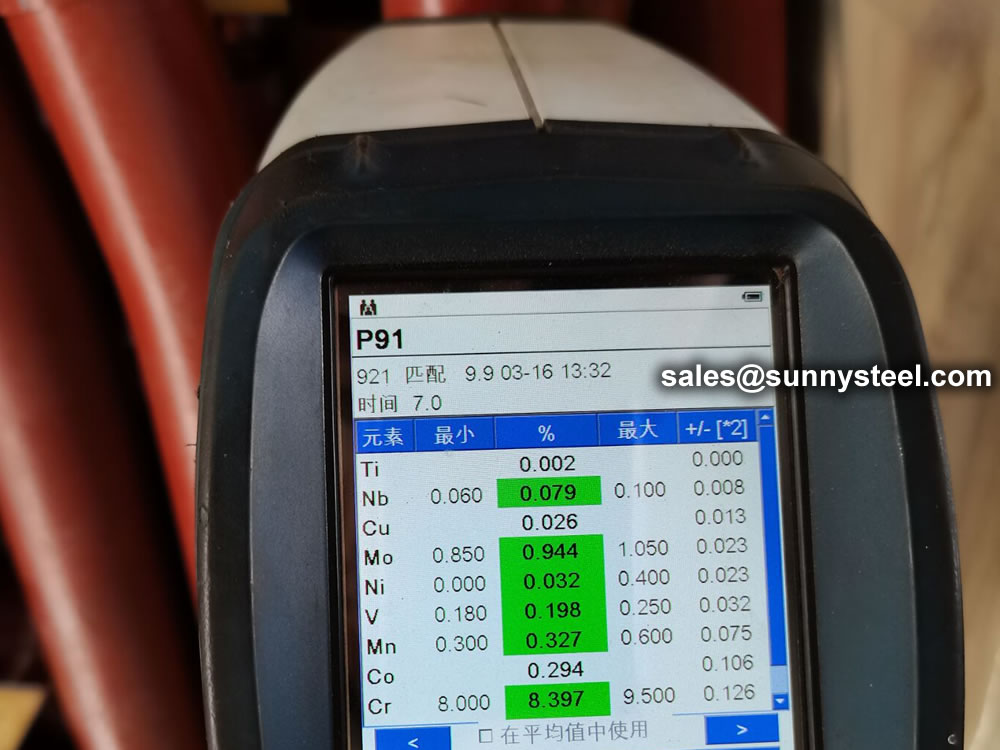
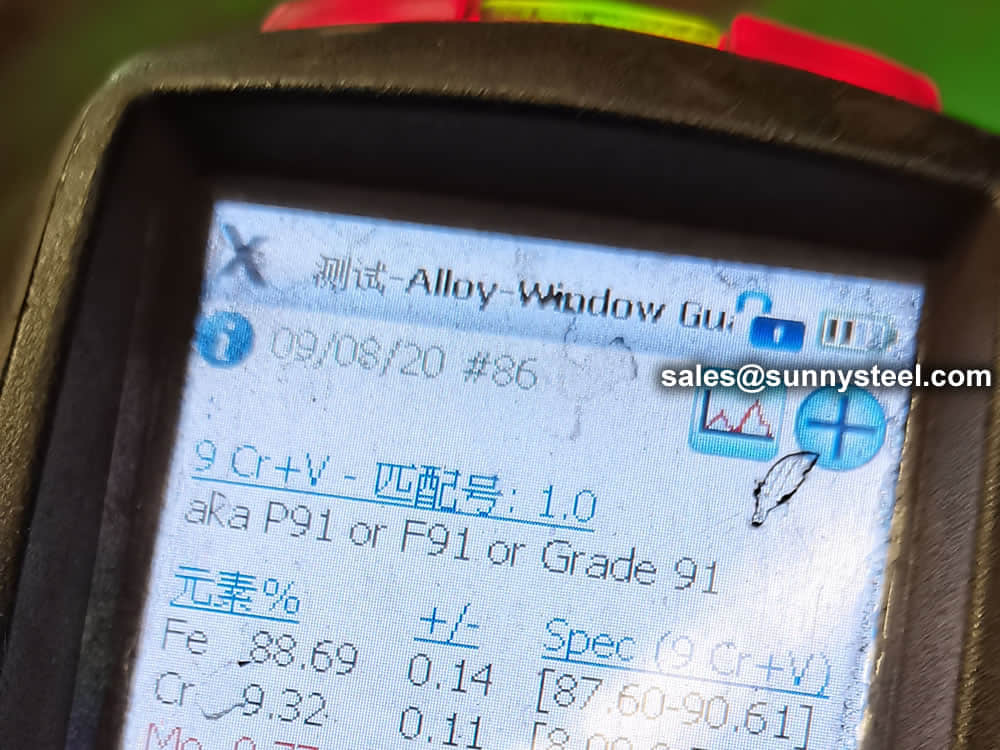
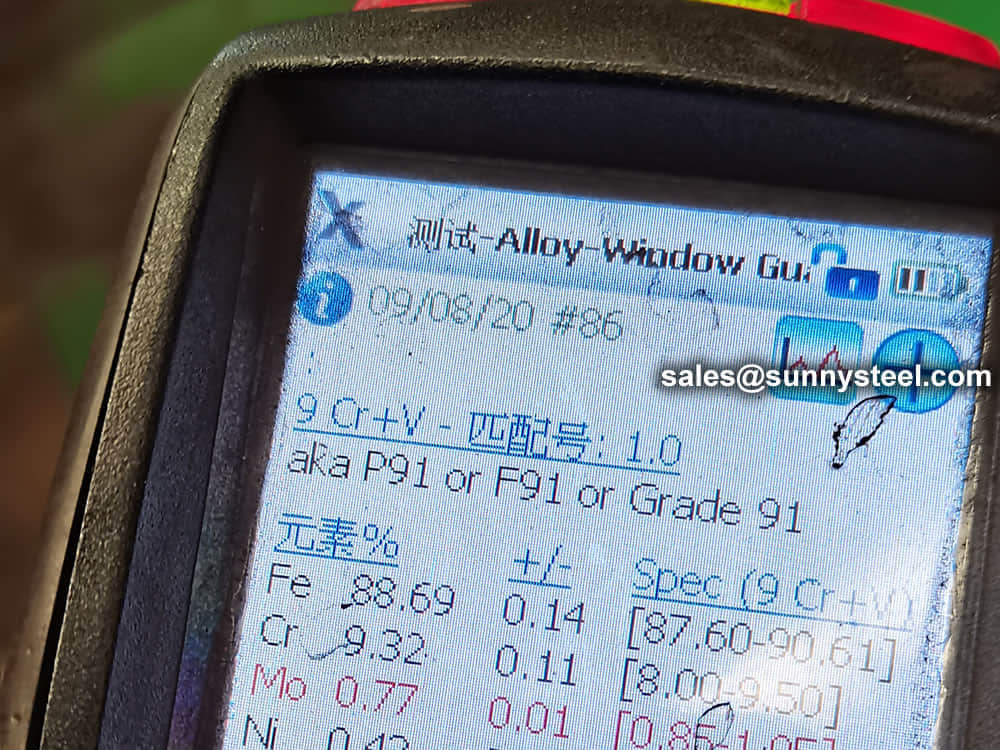















Steel pipe delivery status(condition): cold / hard (BK), cold / soft (BKW), after cold stress relief annealing (BKS), annealing (GBK), normalized (NBK).
| Term | Symbol | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Cold-finished/hard (cold-finished as-drawn) | BK | No heat treatment after the last cold-forming process. The tubes therefore have only low deformability. |
| Cold-finished/soft (lightly cold-worked) | BKW | After the last heat treatment there is a light finishing pass (cold drawing) With proper subsequent processing, the tube can be cold-formed (e.g. bent, expanded) within certain limits. |
| Annealed | GBK | After the final cold-forming process the tubes are annealed in a controlled atmosphere or under vacuum. |
| Normalized | NBK | The tubes are annealed above the upper transformation point in a controlled atmosphere or under vacuum. |
The general cold strip mills, volume should go through continuous annealing (CAPL unit) to eliminate cold hardening and rolling stress, or batch annealing reach the mechanical properties of the corresponding standard specifies. Cold rolled steel surface quality, appearance, dimensional accuracy better than hot-rolled plate, and right-rolled thin product thickness is about 0.18mm, so the majority of users favor.
Cold rolled steel coil substrate products deep processing of high value-added products. Such as electro-galvanized, hot dip galvanized, electro-galvanized fingerprint resistant, painted steel roll damping composite steel, PVC laminating steel plates, etc., so that the excellent quality of these products has a beautiful, high resistance to corrosion, has been widely used.
Cold rolled steel coil finishing after annealing, cut the head, tail, trimming, flattening, smooth, heavy volume, or longitudinal clipboard. Cold-rolled products are widely used in automobile manufacturing, household electrical appliances, instruments, switches, buildings, office furniture and other industries. Steel plate strapping package weight of 3 to 5 tons. Flat sub-volume typically 3 to 10 tons / volume. Coil diameter 6m.
Bare packing/bundle packing/crate packing/wooden protection at the both sides of tubes and suitably protected for sea-worthly delivery or as requested.
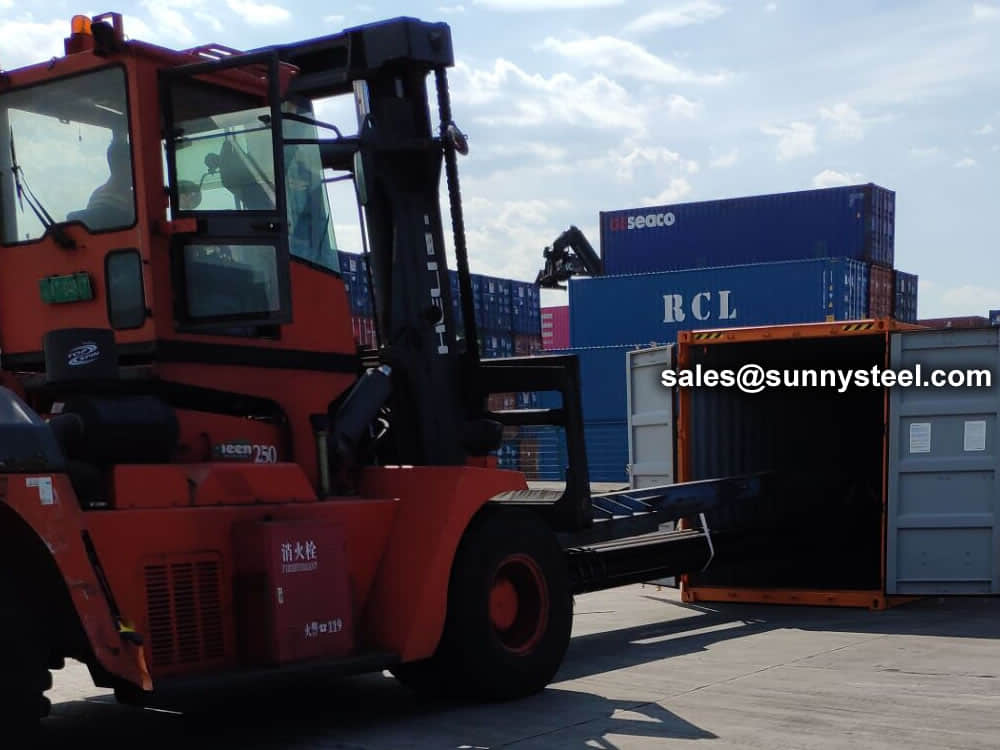
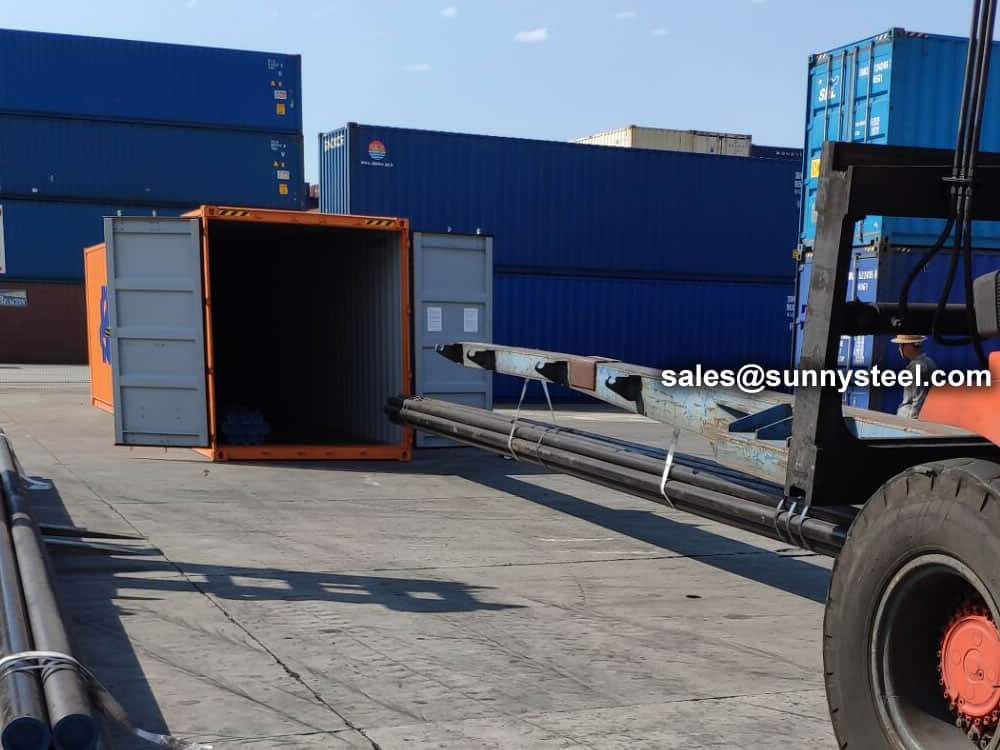
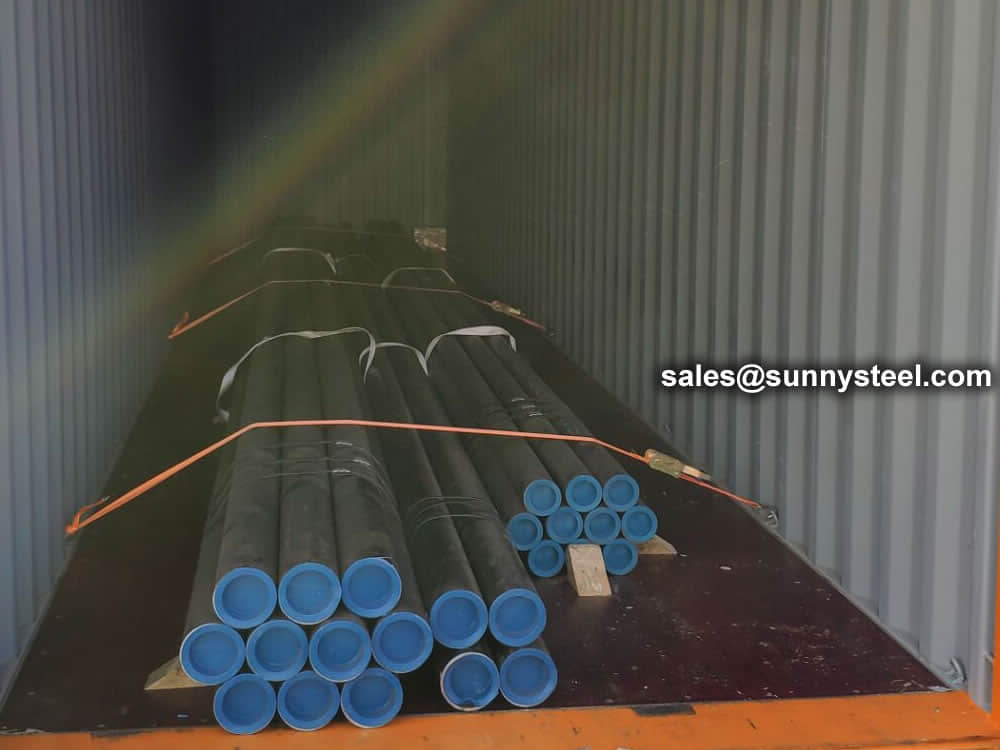
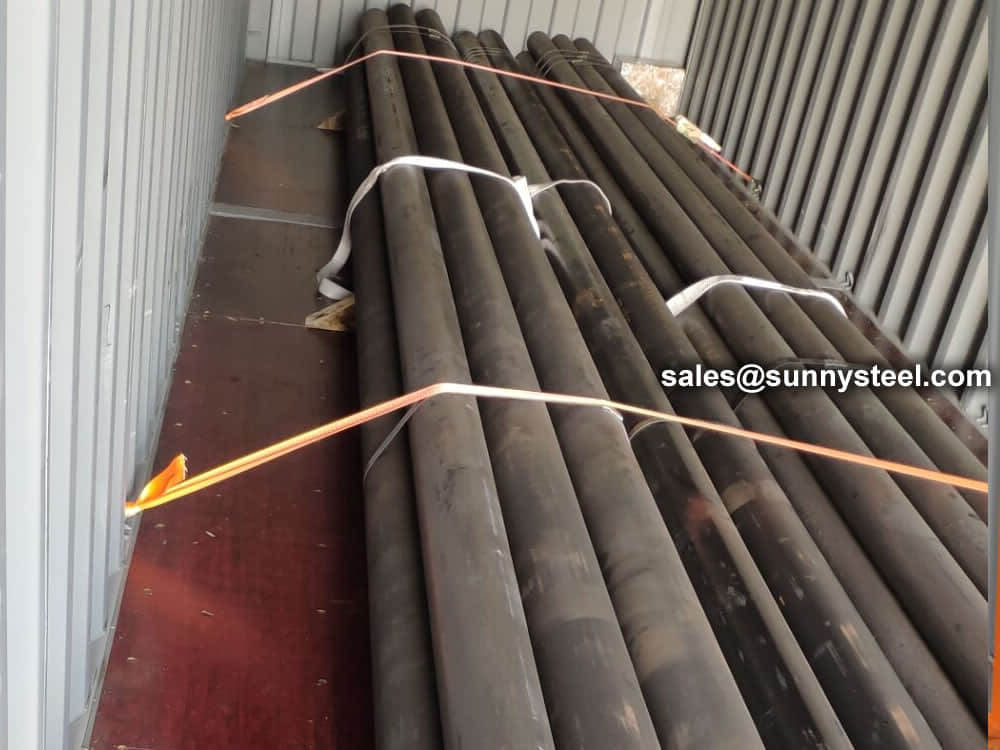












There are probably hundreds of different methods for packing a pipe, and most of them have merit, but there are two principles that are vital for any method to work prevent rusting and Sea transportation security.
Our packing can meet any needs of the customers.
Our team of experienced sales specialists proudly partners with gas and chemical processors, power generation plants, oil refineries, and related industries to offer piping components and value-added services.
Alloy steels are made by combining carbon steel with one or several alloying elements, such as manganese, silicon, nickel, titanium, copper, chromium and aluminum. These metals are added to produce specific properties that are not found in regular carbon steel. The elements are added in varying proportions (or combinations) making the material take on different aspects such as increased hardness, increased corrosion resistance, increased strength, improved formability (ductility); the weldability can also change.
Commonly used alloying elements and their effects are listed in the table given below.
| Alloying Elements | Effect on the Properties |
|---|---|
| Chromium | Increases Resistance to corrosion and oxidation. Increases hardenability and wear resistance. Increases high temperature strength. |
| Nickel | Increases hardenability. Improves toughness. Increases impact strength at low temperatures. |
| Molybdenum | Increases hardenability, high temperature hardness, and wear resistance. Enhances the effects of other alloying elements. Eliminate temper brittleness in steels. Increases high temperature strength. |
| Manganese | Increases hardenability. Combines with sulfur to reduce its adverse effects. |
| Vanadium | Increases hardenability, high temperature hardness, and wear resistance. Improves fatigue resistance. |
| Titanium | Strongest carbide former. Added to stainless steel to prevent precipitation of chromium carbide. |
| Silicon | Removes oxygen in steel making. Improves toughness. Increases hardness ability |
| Boron | Increases hardenability. Produces fine grain size. |
| Aluminum | Forms nitride in nitriding steels. Produces fine grain size in casting. Removes oxygen in steel melting. |
| Cobalt | Increases heat and wear resistance. |
| Tungsten | Increases hardness at elevated temperatures. Refines grain size. |

When you partner with Sunny Steel, you can stop worrying about meeting deadlines thanks to our responsive and timely service. You'll also say goodbye to unnecessary shopping around. Instead, you'll get white glove service from an expert who understands your needs and can get you the materials you need quickly.
